Web2 vs Web3: What are the main differences?
Jun 17, 2024



The net has advanced extensively since its inception, transitioning from the early days of static websites in Web 1.0 to the dynamic, interactive enjoyment of Web 2.0 that we are familiar with. Web 2.0 made extensive modifications, permitting person-generated content, social media, and e-commerce, making the net more attractive and participatory. However, a new paradigm within Web 3.0 promises to revolutionize the digital panorama once again.
Web 3.0, often known as the "decentralized net" or the "semantic web," seeks to cope with a number of the restrictions of Web 2.0 by leveraging blockchain technology and peer-to-peer networks. This new generation of the web focuses on decentralization, giving users more control over their statistics and improving safety through cryptographic methods. While Web 3.0 offers exciting opportunities and improvements in transparency and information ownership, it also faces massive challenges in usability, pace, and extensive adoption. In this blog, we will discover the critical definitions of Web 2.0 and Web 3.0 and discuss the potential implications for the future of the Internet.
What is Web2?
The current iteration of the World Wide Web (WWW), or just the "web," is called Web2. It focuses on social networking networks, online retailers, search engines, and static web pages.Web2 is the second generation of the Internet, following the non-interactive, read-only Web1. It included more dynamic components and interaction; everything was "clickable." This made it possible for people to converse and produce information online.
What is Web3?
Web3, the next Internet generation, is an improved version of the World Wide Web. Because its foundation comprises decentralized technologies like peer-to-peer networks and blockchain, it is often called the "semantic Web" or the "decentralized Web." Thanks to a decentralized design, members may directly access and share resources without a central authority.
Differences between Web 2.0 and Web 3.0
Web2 and Web3 differ significantly because the former has a decentralized structure while the latter has centralized entities with almost complete control. If this were the sole distinction, Web 3.0 should be extensively used by now.
Web3 has the potential to be a very successful online technology, but there are also valid reasons why some experts think it will never take off. Others believe that Web3 may survive with Web2 and never replace it.
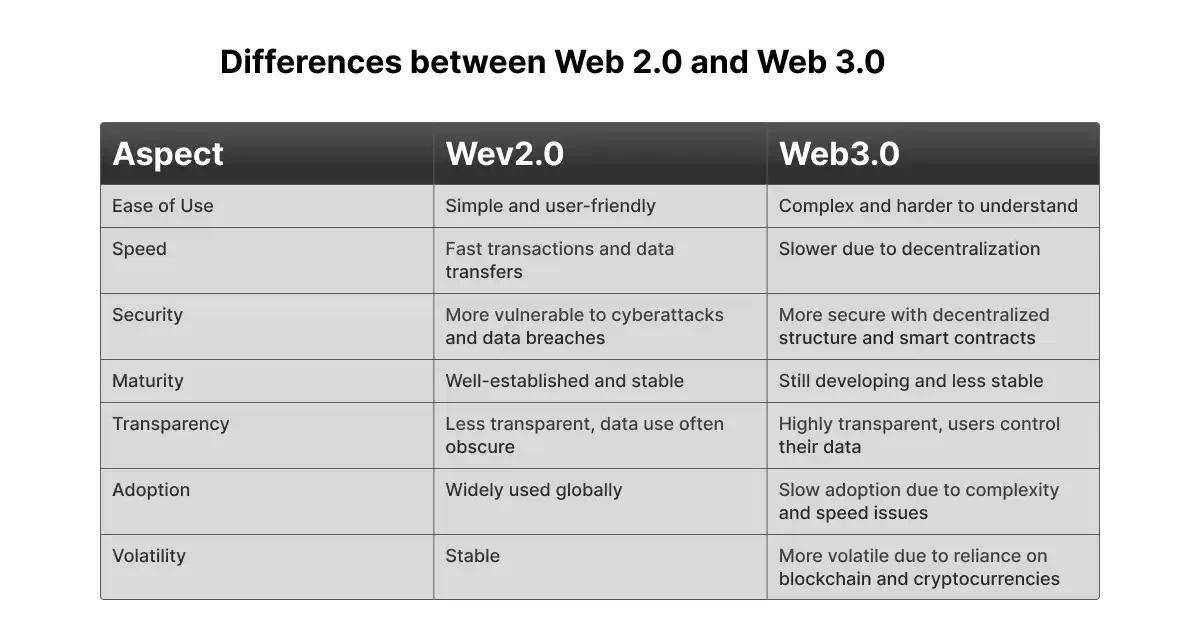
To have a better understanding of these two concepts, let's examine Web 2.0 and Web 3.0 in more detail on the following points:
Ease of Use
The complexity of the underlying technology prevents Web 3.0 from becoming a reality. Web 3.0 is significantly more sophisticated than Web 2.0, so it is more difficult to use and understand.
Yes, there are many exciting possibilities with Web 3.0, and people would love to control their data. However, people will only use technology if it is simple enough to grasp. This is a Web 3.0 problem.
Speed
Web 3.0 has far slower transactions, data transfers, etc., than Web 2.0. Web 2.0 rapidly searches for information using centralized servers, HTTP, and unique web addresses.
Decentralization slows transactions and modifications to data states. Due to the decentralized nature of Web 3.0, changes to data must be processed and dispersed via the distributed ledger.
For Web3, speed is a critical concern. Transaction and data change speeds should be relatively quick for customers and businesses. The comfort that this slowness completely undermines Web 2.0 offers and to which society has become used.
Imagine how much worse performance would be when more transactions were being made if Web 3.0 had speed problems today because it is not widely used.
Security
Web 3.0 is significantly more secure than Web 2.0. Centralized organizations are more vulnerable to cyberattacks and data breaches than decentralized ones. With Web3, smart contracts drastically reduce fraud, hackers, and violations.
Digital security is essential for both customers and organizations. When comparing Web3 to Web2, the security experience is significantly better.
Maturity
Web 3.0 is less solid and developed than Web 2.0. Instability may seriously impair company operations and foster mistrust among customers. Web2 provides a dependable and recognizable experience for users. Web3 is still developing and established.
Web3 is growing at an exciting rate and offers innovation opportunities, but this is also a volatile phase that could negatively affect other processes.
Transparency
Web 3.0 is more transparent than Web 2.0. Consumers often want to know how their data is used, how much it costs, and who has access to it. However, large IT businesses obscure this information on Web 2.0 and keep their monetization methods under wraps. Web3 offers a transparent online environment where users can manage who accesses and uses their data. It is also possible for users to choose which parts of their data they want to share and monetize.
Adoption
The global population uses Web 2.0 extensively, but Web 3.0 is still figuring out its place. Your company must go where the people are if you want to reach as many people as possible; at this time, that is Web2.
The adoption of Web3 is occurring much more slowly than that of Web2. Web3's speed-related problems and complexity are preventing it from being extensively used. Numerous technology experts contend that these problems will keep Web3 from ever being as popular as Web2 is at this point.
If these problems could be resolved successfully, Web3 might swiftly replace Web2 nonetheless. However, it should be highlighted that these problems are not easily resolved and that the speed problem, in particular, is tied to the fundamental decentralization that is essential to Web3.
Volatility
Because Web3 depends on blockchain technology, which is sometimes combined with cryptocurrencies, it is significantly more volatile than Web2. Numerous companies and customers are startled by the erratic swings in cryptocurrencies.
Investing in cryptocurrencies carries risk, which is too significant for many firms. Web 3.0 suffers from this volatility, another barrier to widespread adoption.
Conclusion
Through the use of decentralization and blockchain technology, the digital environment has undergone a dramatic transformation from Web 2.0 to Web 3.0. This will improve user management, security, and transparency. Web 3.0 aims to provide people with more management over their data and safe transactions since Web 2.0 has made the Internet an interactive, user-friendly environment controlled by centralized corporations. However, for Web 3.0 to be widely adopted, it must overcome several vital difficulties, including its complexity, slow speeds, and instability. Web 2.0 and Web 3.0 will probably coexist as time passes, each serving distinct purposes and reshaping the Internet's future. A top Web3 Identity development company, DecentraBlock, is dedicated to accelerating this transition by offering advanced blockchain solutions that close the gap between these two web paradigms. These solutions guarantee anyone a safe, open, and user-focused online experience.
The net has advanced extensively since its inception, transitioning from the early days of static websites in Web 1.0 to the dynamic, interactive enjoyment of Web 2.0 that we are familiar with. Web 2.0 made extensive modifications, permitting person-generated content, social media, and e-commerce, making the net more attractive and participatory. However, a new paradigm within Web 3.0 promises to revolutionize the digital panorama once again.
Web 3.0, often known as the "decentralized net" or the "semantic web," seeks to cope with a number of the restrictions of Web 2.0 by leveraging blockchain technology and peer-to-peer networks. This new generation of the web focuses on decentralization, giving users more control over their statistics and improving safety through cryptographic methods. While Web 3.0 offers exciting opportunities and improvements in transparency and information ownership, it also faces massive challenges in usability, pace, and extensive adoption. In this blog, we will discover the critical definitions of Web 2.0 and Web 3.0 and discuss the potential implications for the future of the Internet.
What is Web2?
The current iteration of the World Wide Web (WWW), or just the "web," is called Web2. It focuses on social networking networks, online retailers, search engines, and static web pages.Web2 is the second generation of the Internet, following the non-interactive, read-only Web1. It included more dynamic components and interaction; everything was "clickable." This made it possible for people to converse and produce information online.
What is Web3?
Web3, the next Internet generation, is an improved version of the World Wide Web. Because its foundation comprises decentralized technologies like peer-to-peer networks and blockchain, it is often called the "semantic Web" or the "decentralized Web." Thanks to a decentralized design, members may directly access and share resources without a central authority.
Differences between Web 2.0 and Web 3.0
Web2 and Web3 differ significantly because the former has a decentralized structure while the latter has centralized entities with almost complete control. If this were the sole distinction, Web 3.0 should be extensively used by now.
Web3 has the potential to be a very successful online technology, but there are also valid reasons why some experts think it will never take off. Others believe that Web3 may survive with Web2 and never replace it.

To have a better understanding of these two concepts, let's examine Web 2.0 and Web 3.0 in more detail on the following points:
Ease of Use
The complexity of the underlying technology prevents Web 3.0 from becoming a reality. Web 3.0 is significantly more sophisticated than Web 2.0, so it is more difficult to use and understand.
Yes, there are many exciting possibilities with Web 3.0, and people would love to control their data. However, people will only use technology if it is simple enough to grasp. This is a Web 3.0 problem.
Speed
Web 3.0 has far slower transactions, data transfers, etc., than Web 2.0. Web 2.0 rapidly searches for information using centralized servers, HTTP, and unique web addresses.
Decentralization slows transactions and modifications to data states. Due to the decentralized nature of Web 3.0, changes to data must be processed and dispersed via the distributed ledger.
For Web3, speed is a critical concern. Transaction and data change speeds should be relatively quick for customers and businesses. The comfort that this slowness completely undermines Web 2.0 offers and to which society has become used.
Imagine how much worse performance would be when more transactions were being made if Web 3.0 had speed problems today because it is not widely used.
Security
Web 3.0 is significantly more secure than Web 2.0. Centralized organizations are more vulnerable to cyberattacks and data breaches than decentralized ones. With Web3, smart contracts drastically reduce fraud, hackers, and violations.
Digital security is essential for both customers and organizations. When comparing Web3 to Web2, the security experience is significantly better.
Maturity
Web 3.0 is less solid and developed than Web 2.0. Instability may seriously impair company operations and foster mistrust among customers. Web2 provides a dependable and recognizable experience for users. Web3 is still developing and established.
Web3 is growing at an exciting rate and offers innovation opportunities, but this is also a volatile phase that could negatively affect other processes.
Transparency
Web 3.0 is more transparent than Web 2.0. Consumers often want to know how their data is used, how much it costs, and who has access to it. However, large IT businesses obscure this information on Web 2.0 and keep their monetization methods under wraps. Web3 offers a transparent online environment where users can manage who accesses and uses their data. It is also possible for users to choose which parts of their data they want to share and monetize.
Adoption
The global population uses Web 2.0 extensively, but Web 3.0 is still figuring out its place. Your company must go where the people are if you want to reach as many people as possible; at this time, that is Web2.
The adoption of Web3 is occurring much more slowly than that of Web2. Web3's speed-related problems and complexity are preventing it from being extensively used. Numerous technology experts contend that these problems will keep Web3 from ever being as popular as Web2 is at this point.
If these problems could be resolved successfully, Web3 might swiftly replace Web2 nonetheless. However, it should be highlighted that these problems are not easily resolved and that the speed problem, in particular, is tied to the fundamental decentralization that is essential to Web3.
Volatility
Because Web3 depends on blockchain technology, which is sometimes combined with cryptocurrencies, it is significantly more volatile than Web2. Numerous companies and customers are startled by the erratic swings in cryptocurrencies.
Investing in cryptocurrencies carries risk, which is too significant for many firms. Web 3.0 suffers from this volatility, another barrier to widespread adoption.
Conclusion
Through the use of decentralization and blockchain technology, the digital environment has undergone a dramatic transformation from Web 2.0 to Web 3.0. This will improve user management, security, and transparency. Web 3.0 aims to provide people with more management over their data and safe transactions since Web 2.0 has made the Internet an interactive, user-friendly environment controlled by centralized corporations. However, for Web 3.0 to be widely adopted, it must overcome several vital difficulties, including its complexity, slow speeds, and instability. Web 2.0 and Web 3.0 will probably coexist as time passes, each serving distinct purposes and reshaping the Internet's future. A top Web3 Identity development company, DecentraBlock, is dedicated to accelerating this transition by offering advanced blockchain solutions that close the gap between these two web paradigms. These solutions guarantee anyone a safe, open, and user-focused online experience.
The net has advanced extensively since its inception, transitioning from the early days of static websites in Web 1.0 to the dynamic, interactive enjoyment of Web 2.0 that we are familiar with. Web 2.0 made extensive modifications, permitting person-generated content, social media, and e-commerce, making the net more attractive and participatory. However, a new paradigm within Web 3.0 promises to revolutionize the digital panorama once again.
Web 3.0, often known as the "decentralized net" or the "semantic web," seeks to cope with a number of the restrictions of Web 2.0 by leveraging blockchain technology and peer-to-peer networks. This new generation of the web focuses on decentralization, giving users more control over their statistics and improving safety through cryptographic methods. While Web 3.0 offers exciting opportunities and improvements in transparency and information ownership, it also faces massive challenges in usability, pace, and extensive adoption. In this blog, we will discover the critical definitions of Web 2.0 and Web 3.0 and discuss the potential implications for the future of the Internet.
What is Web2?
The current iteration of the World Wide Web (WWW), or just the "web," is called Web2. It focuses on social networking networks, online retailers, search engines, and static web pages.Web2 is the second generation of the Internet, following the non-interactive, read-only Web1. It included more dynamic components and interaction; everything was "clickable." This made it possible for people to converse and produce information online.
What is Web3?
Web3, the next Internet generation, is an improved version of the World Wide Web. Because its foundation comprises decentralized technologies like peer-to-peer networks and blockchain, it is often called the "semantic Web" or the "decentralized Web." Thanks to a decentralized design, members may directly access and share resources without a central authority.
Differences between Web 2.0 and Web 3.0
Web2 and Web3 differ significantly because the former has a decentralized structure while the latter has centralized entities with almost complete control. If this were the sole distinction, Web 3.0 should be extensively used by now.
Web3 has the potential to be a very successful online technology, but there are also valid reasons why some experts think it will never take off. Others believe that Web3 may survive with Web2 and never replace it.

To have a better understanding of these two concepts, let's examine Web 2.0 and Web 3.0 in more detail on the following points:
Ease of Use
The complexity of the underlying technology prevents Web 3.0 from becoming a reality. Web 3.0 is significantly more sophisticated than Web 2.0, so it is more difficult to use and understand.
Yes, there are many exciting possibilities with Web 3.0, and people would love to control their data. However, people will only use technology if it is simple enough to grasp. This is a Web 3.0 problem.
Speed
Web 3.0 has far slower transactions, data transfers, etc., than Web 2.0. Web 2.0 rapidly searches for information using centralized servers, HTTP, and unique web addresses.
Decentralization slows transactions and modifications to data states. Due to the decentralized nature of Web 3.0, changes to data must be processed and dispersed via the distributed ledger.
For Web3, speed is a critical concern. Transaction and data change speeds should be relatively quick for customers and businesses. The comfort that this slowness completely undermines Web 2.0 offers and to which society has become used.
Imagine how much worse performance would be when more transactions were being made if Web 3.0 had speed problems today because it is not widely used.
Security
Web 3.0 is significantly more secure than Web 2.0. Centralized organizations are more vulnerable to cyberattacks and data breaches than decentralized ones. With Web3, smart contracts drastically reduce fraud, hackers, and violations.
Digital security is essential for both customers and organizations. When comparing Web3 to Web2, the security experience is significantly better.
Maturity
Web 3.0 is less solid and developed than Web 2.0. Instability may seriously impair company operations and foster mistrust among customers. Web2 provides a dependable and recognizable experience for users. Web3 is still developing and established.
Web3 is growing at an exciting rate and offers innovation opportunities, but this is also a volatile phase that could negatively affect other processes.
Transparency
Web 3.0 is more transparent than Web 2.0. Consumers often want to know how their data is used, how much it costs, and who has access to it. However, large IT businesses obscure this information on Web 2.0 and keep their monetization methods under wraps. Web3 offers a transparent online environment where users can manage who accesses and uses their data. It is also possible for users to choose which parts of their data they want to share and monetize.
Adoption
The global population uses Web 2.0 extensively, but Web 3.0 is still figuring out its place. Your company must go where the people are if you want to reach as many people as possible; at this time, that is Web2.
The adoption of Web3 is occurring much more slowly than that of Web2. Web3's speed-related problems and complexity are preventing it from being extensively used. Numerous technology experts contend that these problems will keep Web3 from ever being as popular as Web2 is at this point.
If these problems could be resolved successfully, Web3 might swiftly replace Web2 nonetheless. However, it should be highlighted that these problems are not easily resolved and that the speed problem, in particular, is tied to the fundamental decentralization that is essential to Web3.
Volatility
Because Web3 depends on blockchain technology, which is sometimes combined with cryptocurrencies, it is significantly more volatile than Web2. Numerous companies and customers are startled by the erratic swings in cryptocurrencies.
Investing in cryptocurrencies carries risk, which is too significant for many firms. Web 3.0 suffers from this volatility, another barrier to widespread adoption.
Conclusion
Through the use of decentralization and blockchain technology, the digital environment has undergone a dramatic transformation from Web 2.0 to Web 3.0. This will improve user management, security, and transparency. Web 3.0 aims to provide people with more management over their data and safe transactions since Web 2.0 has made the Internet an interactive, user-friendly environment controlled by centralized corporations. However, for Web 3.0 to be widely adopted, it must overcome several vital difficulties, including its complexity, slow speeds, and instability. Web 2.0 and Web 3.0 will probably coexist as time passes, each serving distinct purposes and reshaping the Internet's future. A top Web3 Identity development company, DecentraBlock, is dedicated to accelerating this transition by offering advanced blockchain solutions that close the gap between these two web paradigms. These solutions guarantee anyone a safe, open, and user-focused online experience.

DecentraBlock is at the forefront of blockchain innovation, revolutionizing how businesses secure, transact, and grow in the digital age. Join us on a journey to harness the full potential of decentralized technology for a more efficient and transparent future.
Services
Subscribe to Our Newsletter
Get the latest news, updates, and insights on blockchain technology directly to your inbox. Sign up for our newsletter today!
© 2024 DecentraBlock. All rights reserved.

DecentraBlock is at the forefront of blockchain innovation, revolutionizing how businesses secure, transact, and grow in the digital age. Join us on a journey to harness the full potential of decentralized technology for a more efficient and transparent future.
Services
Subscribe to Our Newsletter
Get the latest news, updates, and insights on blockchain technology directly to your inbox. Sign up for our newsletter today!
© 2024 DecentraBlock. All rights reserved.

DecentraBlock is at the forefront of blockchain innovation, revolutionizing how businesses secure, transact, and grow in the digital age. Join us on a journey to harness the full potential of decentralized technology for a more efficient and transparent future.
Services
Subscribe to Our Newsletter
Get the latest news, updates, and insights on blockchain technology directly to your inbox. Sign up for our newsletter today!
© 2024 DecentraBlock. All rights reserved.


