ZK-Rollups: The Next Step In Blockchain Scalability
Sep 2, 2024



Blockchain networks face a scalability trilemma in which they cannot have everything unexpectedly: robust security, genuine decentralisation, and high throughput. However, layer 2 blockchain projects are the most promising answers to higher blockchain scalability.
Layer 2 blockchains are becoming more diverse, with ZK-rollups performing as a separate technology stack alongside optimistic rollups, surest, valium, and plasma. This article recognises ZK rollups cognisance – layer 2 rollups using zero expertise proofs (ZK-proofs or ZKP).
What Are ZK-Rollups?
ZK-rollup is a layer 2 scaling answer that facilitates faster transaction techniques by dealing with them off the principal blockchain (off-chain) but statistics the transaction records on the primary blockchain (on-chain). It uses ZK-proofs to ensure those transactions are legitimate without revealing private facts.
Key Features Of ZK-Rollups
The most special capabilities of ZK-rollups are validity proofs and the availability of on-chain facts.
Validity Proofs: These are checks accomplished by way of zero-knowledge proofs, a form of cryptographic evidence that can affirm the result of a calculation quickly and without revealing specific details of that calculation. There are various sorts of those proofs, along with zk-SNARKs and zk-STARKs have their particular residences.
On-Chain Data Availability: While the actual transactions are processed off the main blockchain, ZK-rollups ensure a few important pieces of statistics are stored on the main (layer 1) blockchain. This storage is fundamental to the consensus mechanism and serves ZK-rollups' purpose. With this setup, each person can independently confirm all the transactions in a rollup, and it's even well-matched with Ethereum's Virtual Machine, allowing it to guide a wide variety of applications.
How ZK-Rollups Support Increased Blockchain Scalability?
Off-Chain Computation, Reduced Gas & Data Compression: Unlike plasma and valiums, rollups (ZK and optimistic) don't completely put in force layer 2 scaling. Rollups don't offer 100% off-chain statistics storage. Instead, they simplest circulate nation garage and computation off-chain. Hence, the roll-up answer has a strict cap on scalability: it's limited via the statistics bandwidth of the underlying blockchain.
Despite this, rollups provide an enormous leap forward compared to the base layer. For example, the approval of the ERC20 token on Ethereum charges 45,000 gas, whereas maximum rollups take less than 300 gas for the same operation. In addition, a roll-up compresses transaction data. A standard ETH transfer takes around a hundred and ten bytes, compared to twelve in a rollup. Here, the signature compression provides the most significant size reduction. On Ethereum, a signature takes 68 bytes. Contrastingly, a roll-up can batch ~a hundred transactions beneath an unmarried signature, lowering the dimensions to 0.5 bytes.
Enhanced Security: A critical characteristic of ZK-rollups is the safety assurance that the person can always return the asset to layer 1. This is critical because different layer 2 answers don't offer that assurance. For instance, valiums can lose assets in case of a facts availability failure. ZK-rollups won't face any facts availability problems, meaning attackers can not cause enormous damage. Moreover, facts availability eliminates the need to map assets to proprietors, resulting in a significant gain of rollups over different L2 solutions.
How To Work ZK-Rollups?
At their centre, ZK-rollups work through a smart contract at the layer 1 blockchain. This clever settlement is crucial because it keeps an authoritative document known as the state root.
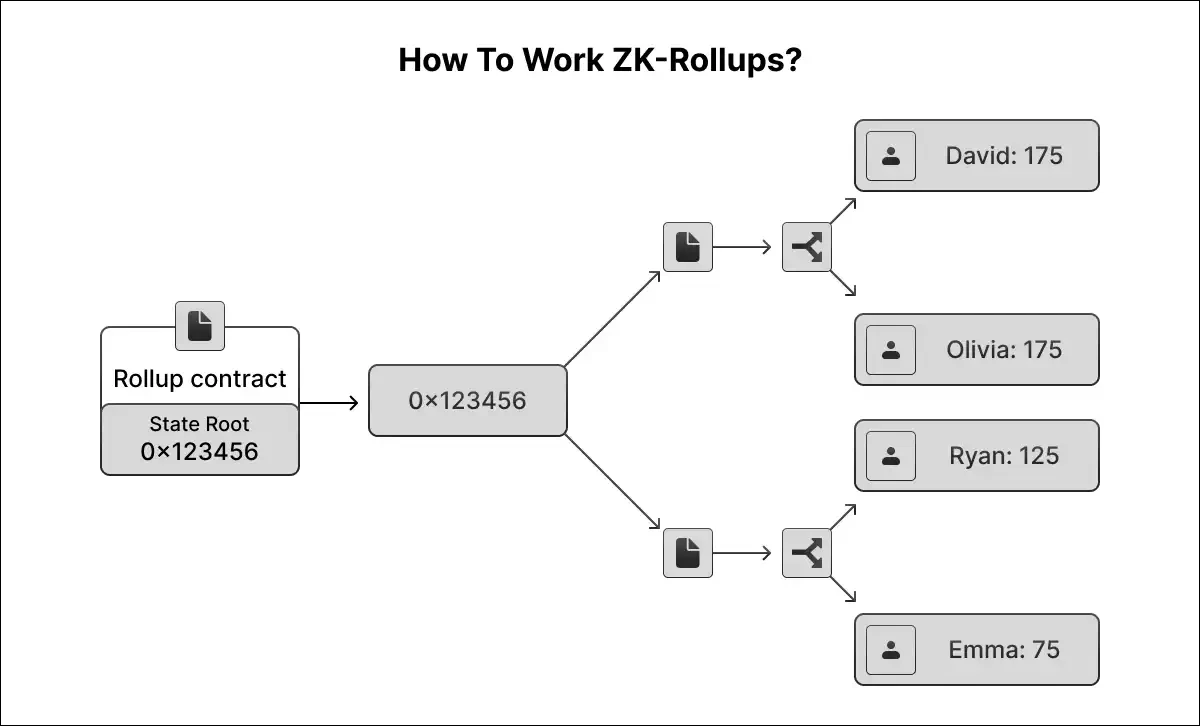
State Root: The state root is a Merkle tree of batches of records approximately the rollup's accounts, balances, and contract code. Users, like the sequencer, put up new batches (a compressed series of transactions) along with the old and new country roots (pre- and submit-country roots). The smart contract assesses the organisation's root towards today's root. It switches the modern version to the new country root if they match.
Deposits & Withdrawals: Naturally, rollups should permit inputs and outputs from the "outdoor" to enable withdrawals and deposits. The transaction that submits the batch containing "out of doors" inputs additionally moves belongings to the smart contract. The contract initiates withdrawal when the transaction submits the " outdoor " output batch. Hence, the underlying smart contract synchronises kingdom changes throughout the base layer and the rollup.
Post-State Verification: How can the correctness of the publish-kingdom root be verified? Until now, a malicious actor could pony model of the kingdom root (e.g., wherein the.g.transfer all assets to their account). However, rollups have addressed this difficulty in two exclusive ways: validity proofs and fraud proofs. Hence, we've got schemes: zero-knowledge and constructive rollups.
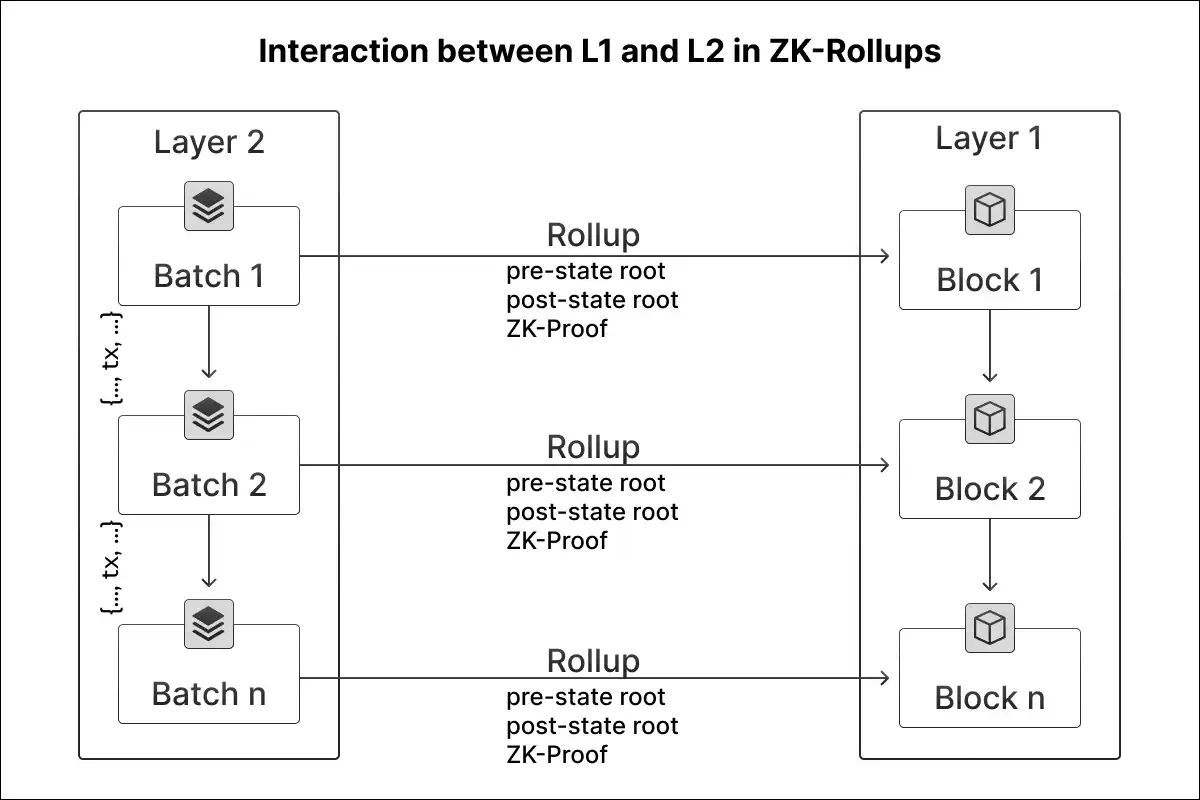
Validity Proofs: ZK-rollups depend on validity proofs to ensure the publish-country root carries no manipulations. Therefore, every new batch of transactions comes with a zk-SNARK (or zk-STARK) – an argument of information proving the batch computation produces the same result as the new state root. And the most critical component: even the heaviest computations can be confirmed quickly on-chain thanks to the extraordinarily complex math behind ZK-proofs.
ZK-Rollups Real-World Applications
There are a dozen energetic ZK-rollups with a total cost of $1.3 billion. Most of those tasks are in the early stages, under "complete education wheels" (i.e., run via operators).
Among tasks, the clear winners regarding TPS potential are zkSync Era, dYdX, and Starknet. These networks all have over $100M in TVL and method around 10M monthly transactions. Most rollups hire zk-SNARKs; the best exceptions are Starknet and dYdX, which both use zk-STARKs.
Conclusion
ZK-rollups is a layer 2 scaling solution that uses validity proofs for off-chain computation and shops a small amount of transaction information on the chain.
The complexity of SNARK-proving and the availability of on-chain facts are the main prices of ZK-rollup operations, making them less appealing to widespread-cause EVMs. For that motive, positive roll-ups take the lead regarding marketplace adoption. On top of that, even the most popular ZK-rollup initiatives – zkSync technology, Starknet, and Loopring – are handiest in the early ranges of improvement and don't run autonomously.
However, the destiny of ZK-rollups could be very shiny. Advancements within the complicated zero-information era will make ZK-rollups more compatible with EVM and time-honoured programs. The privacy-retaining feature, instant withdrawals and decrease in line with on-chain transaction fees make ZK-rollups a perfect option for layer 2 scaling. Contact Us
Blockchain networks face a scalability trilemma in which they cannot have everything unexpectedly: robust security, genuine decentralisation, and high throughput. However, layer 2 blockchain projects are the most promising answers to higher blockchain scalability.
Layer 2 blockchains are becoming more diverse, with ZK-rollups performing as a separate technology stack alongside optimistic rollups, surest, valium, and plasma. This article recognises ZK rollups cognisance – layer 2 rollups using zero expertise proofs (ZK-proofs or ZKP).
What Are ZK-Rollups?
ZK-rollup is a layer 2 scaling answer that facilitates faster transaction techniques by dealing with them off the principal blockchain (off-chain) but statistics the transaction records on the primary blockchain (on-chain). It uses ZK-proofs to ensure those transactions are legitimate without revealing private facts.
Key Features Of ZK-Rollups
The most special capabilities of ZK-rollups are validity proofs and the availability of on-chain facts.
Validity Proofs: These are checks accomplished by way of zero-knowledge proofs, a form of cryptographic evidence that can affirm the result of a calculation quickly and without revealing specific details of that calculation. There are various sorts of those proofs, along with zk-SNARKs and zk-STARKs have their particular residences.
On-Chain Data Availability: While the actual transactions are processed off the main blockchain, ZK-rollups ensure a few important pieces of statistics are stored on the main (layer 1) blockchain. This storage is fundamental to the consensus mechanism and serves ZK-rollups' purpose. With this setup, each person can independently confirm all the transactions in a rollup, and it's even well-matched with Ethereum's Virtual Machine, allowing it to guide a wide variety of applications.
How ZK-Rollups Support Increased Blockchain Scalability?
Off-Chain Computation, Reduced Gas & Data Compression: Unlike plasma and valiums, rollups (ZK and optimistic) don't completely put in force layer 2 scaling. Rollups don't offer 100% off-chain statistics storage. Instead, they simplest circulate nation garage and computation off-chain. Hence, the roll-up answer has a strict cap on scalability: it's limited via the statistics bandwidth of the underlying blockchain.
Despite this, rollups provide an enormous leap forward compared to the base layer. For example, the approval of the ERC20 token on Ethereum charges 45,000 gas, whereas maximum rollups take less than 300 gas for the same operation. In addition, a roll-up compresses transaction data. A standard ETH transfer takes around a hundred and ten bytes, compared to twelve in a rollup. Here, the signature compression provides the most significant size reduction. On Ethereum, a signature takes 68 bytes. Contrastingly, a roll-up can batch ~a hundred transactions beneath an unmarried signature, lowering the dimensions to 0.5 bytes.
Enhanced Security: A critical characteristic of ZK-rollups is the safety assurance that the person can always return the asset to layer 1. This is critical because different layer 2 answers don't offer that assurance. For instance, valiums can lose assets in case of a facts availability failure. ZK-rollups won't face any facts availability problems, meaning attackers can not cause enormous damage. Moreover, facts availability eliminates the need to map assets to proprietors, resulting in a significant gain of rollups over different L2 solutions.
How To Work ZK-Rollups?
At their centre, ZK-rollups work through a smart contract at the layer 1 blockchain. This clever settlement is crucial because it keeps an authoritative document known as the state root.

State Root: The state root is a Merkle tree of batches of records approximately the rollup's accounts, balances, and contract code. Users, like the sequencer, put up new batches (a compressed series of transactions) along with the old and new country roots (pre- and submit-country roots). The smart contract assesses the organisation's root towards today's root. It switches the modern version to the new country root if they match.
Deposits & Withdrawals: Naturally, rollups should permit inputs and outputs from the "outdoor" to enable withdrawals and deposits. The transaction that submits the batch containing "out of doors" inputs additionally moves belongings to the smart contract. The contract initiates withdrawal when the transaction submits the " outdoor " output batch. Hence, the underlying smart contract synchronises kingdom changes throughout the base layer and the rollup.
Post-State Verification: How can the correctness of the publish-kingdom root be verified? Until now, a malicious actor could pony model of the kingdom root (e.g., wherein the.g.transfer all assets to their account). However, rollups have addressed this difficulty in two exclusive ways: validity proofs and fraud proofs. Hence, we've got schemes: zero-knowledge and constructive rollups.

Validity Proofs: ZK-rollups depend on validity proofs to ensure the publish-country root carries no manipulations. Therefore, every new batch of transactions comes with a zk-SNARK (or zk-STARK) – an argument of information proving the batch computation produces the same result as the new state root. And the most critical component: even the heaviest computations can be confirmed quickly on-chain thanks to the extraordinarily complex math behind ZK-proofs.
ZK-Rollups Real-World Applications
There are a dozen energetic ZK-rollups with a total cost of $1.3 billion. Most of those tasks are in the early stages, under "complete education wheels" (i.e., run via operators).
Among tasks, the clear winners regarding TPS potential are zkSync Era, dYdX, and Starknet. These networks all have over $100M in TVL and method around 10M monthly transactions. Most rollups hire zk-SNARKs; the best exceptions are Starknet and dYdX, which both use zk-STARKs.
Conclusion
ZK-rollups is a layer 2 scaling solution that uses validity proofs for off-chain computation and shops a small amount of transaction information on the chain.
The complexity of SNARK-proving and the availability of on-chain facts are the main prices of ZK-rollup operations, making them less appealing to widespread-cause EVMs. For that motive, positive roll-ups take the lead regarding marketplace adoption. On top of that, even the most popular ZK-rollup initiatives – zkSync technology, Starknet, and Loopring – are handiest in the early ranges of improvement and don't run autonomously.
However, the destiny of ZK-rollups could be very shiny. Advancements within the complicated zero-information era will make ZK-rollups more compatible with EVM and time-honoured programs. The privacy-retaining feature, instant withdrawals and decrease in line with on-chain transaction fees make ZK-rollups a perfect option for layer 2 scaling. Contact Us
Blockchain networks face a scalability trilemma in which they cannot have everything unexpectedly: robust security, genuine decentralisation, and high throughput. However, layer 2 blockchain projects are the most promising answers to higher blockchain scalability.
Layer 2 blockchains are becoming more diverse, with ZK-rollups performing as a separate technology stack alongside optimistic rollups, surest, valium, and plasma. This article recognises ZK rollups cognisance – layer 2 rollups using zero expertise proofs (ZK-proofs or ZKP).
What Are ZK-Rollups?
ZK-rollup is a layer 2 scaling answer that facilitates faster transaction techniques by dealing with them off the principal blockchain (off-chain) but statistics the transaction records on the primary blockchain (on-chain). It uses ZK-proofs to ensure those transactions are legitimate without revealing private facts.
Key Features Of ZK-Rollups
The most special capabilities of ZK-rollups are validity proofs and the availability of on-chain facts.
Validity Proofs: These are checks accomplished by way of zero-knowledge proofs, a form of cryptographic evidence that can affirm the result of a calculation quickly and without revealing specific details of that calculation. There are various sorts of those proofs, along with zk-SNARKs and zk-STARKs have their particular residences.
On-Chain Data Availability: While the actual transactions are processed off the main blockchain, ZK-rollups ensure a few important pieces of statistics are stored on the main (layer 1) blockchain. This storage is fundamental to the consensus mechanism and serves ZK-rollups' purpose. With this setup, each person can independently confirm all the transactions in a rollup, and it's even well-matched with Ethereum's Virtual Machine, allowing it to guide a wide variety of applications.
How ZK-Rollups Support Increased Blockchain Scalability?
Off-Chain Computation, Reduced Gas & Data Compression: Unlike plasma and valiums, rollups (ZK and optimistic) don't completely put in force layer 2 scaling. Rollups don't offer 100% off-chain statistics storage. Instead, they simplest circulate nation garage and computation off-chain. Hence, the roll-up answer has a strict cap on scalability: it's limited via the statistics bandwidth of the underlying blockchain.
Despite this, rollups provide an enormous leap forward compared to the base layer. For example, the approval of the ERC20 token on Ethereum charges 45,000 gas, whereas maximum rollups take less than 300 gas for the same operation. In addition, a roll-up compresses transaction data. A standard ETH transfer takes around a hundred and ten bytes, compared to twelve in a rollup. Here, the signature compression provides the most significant size reduction. On Ethereum, a signature takes 68 bytes. Contrastingly, a roll-up can batch ~a hundred transactions beneath an unmarried signature, lowering the dimensions to 0.5 bytes.
Enhanced Security: A critical characteristic of ZK-rollups is the safety assurance that the person can always return the asset to layer 1. This is critical because different layer 2 answers don't offer that assurance. For instance, valiums can lose assets in case of a facts availability failure. ZK-rollups won't face any facts availability problems, meaning attackers can not cause enormous damage. Moreover, facts availability eliminates the need to map assets to proprietors, resulting in a significant gain of rollups over different L2 solutions.
How To Work ZK-Rollups?
At their centre, ZK-rollups work through a smart contract at the layer 1 blockchain. This clever settlement is crucial because it keeps an authoritative document known as the state root.

State Root: The state root is a Merkle tree of batches of records approximately the rollup's accounts, balances, and contract code. Users, like the sequencer, put up new batches (a compressed series of transactions) along with the old and new country roots (pre- and submit-country roots). The smart contract assesses the organisation's root towards today's root. It switches the modern version to the new country root if they match.
Deposits & Withdrawals: Naturally, rollups should permit inputs and outputs from the "outdoor" to enable withdrawals and deposits. The transaction that submits the batch containing "out of doors" inputs additionally moves belongings to the smart contract. The contract initiates withdrawal when the transaction submits the " outdoor " output batch. Hence, the underlying smart contract synchronises kingdom changes throughout the base layer and the rollup.
Post-State Verification: How can the correctness of the publish-kingdom root be verified? Until now, a malicious actor could pony model of the kingdom root (e.g., wherein the.g.transfer all assets to their account). However, rollups have addressed this difficulty in two exclusive ways: validity proofs and fraud proofs. Hence, we've got schemes: zero-knowledge and constructive rollups.

Validity Proofs: ZK-rollups depend on validity proofs to ensure the publish-country root carries no manipulations. Therefore, every new batch of transactions comes with a zk-SNARK (or zk-STARK) – an argument of information proving the batch computation produces the same result as the new state root. And the most critical component: even the heaviest computations can be confirmed quickly on-chain thanks to the extraordinarily complex math behind ZK-proofs.
ZK-Rollups Real-World Applications
There are a dozen energetic ZK-rollups with a total cost of $1.3 billion. Most of those tasks are in the early stages, under "complete education wheels" (i.e., run via operators).
Among tasks, the clear winners regarding TPS potential are zkSync Era, dYdX, and Starknet. These networks all have over $100M in TVL and method around 10M monthly transactions. Most rollups hire zk-SNARKs; the best exceptions are Starknet and dYdX, which both use zk-STARKs.
Conclusion
ZK-rollups is a layer 2 scaling solution that uses validity proofs for off-chain computation and shops a small amount of transaction information on the chain.
The complexity of SNARK-proving and the availability of on-chain facts are the main prices of ZK-rollup operations, making them less appealing to widespread-cause EVMs. For that motive, positive roll-ups take the lead regarding marketplace adoption. On top of that, even the most popular ZK-rollup initiatives – zkSync technology, Starknet, and Loopring – are handiest in the early ranges of improvement and don't run autonomously.
However, the destiny of ZK-rollups could be very shiny. Advancements within the complicated zero-information era will make ZK-rollups more compatible with EVM and time-honoured programs. The privacy-retaining feature, instant withdrawals and decrease in line with on-chain transaction fees make ZK-rollups a perfect option for layer 2 scaling. Contact Us

DecentraBlock is at the forefront of blockchain innovation, revolutionizing how businesses secure, transact, and grow in the digital age. Join us on a journey to harness the full potential of decentralized technology for a more efficient and transparent future.
Services
Subscribe to Our Newsletter
Get the latest news, updates, and insights on blockchain technology directly to your inbox. Sign up for our newsletter today!
© 2024 DecentraBlock. All rights reserved.

DecentraBlock is at the forefront of blockchain innovation, revolutionizing how businesses secure, transact, and grow in the digital age. Join us on a journey to harness the full potential of decentralized technology for a more efficient and transparent future.
Services
Subscribe to Our Newsletter
Get the latest news, updates, and insights on blockchain technology directly to your inbox. Sign up for our newsletter today!
© 2024 DecentraBlock. All rights reserved.

DecentraBlock is at the forefront of blockchain innovation, revolutionizing how businesses secure, transact, and grow in the digital age. Join us on a journey to harness the full potential of decentralized technology for a more efficient and transparent future.
Services
Subscribe to Our Newsletter
Get the latest news, updates, and insights on blockchain technology directly to your inbox. Sign up for our newsletter today!
© 2024 DecentraBlock. All rights reserved.


